Neurophysiology of Gait
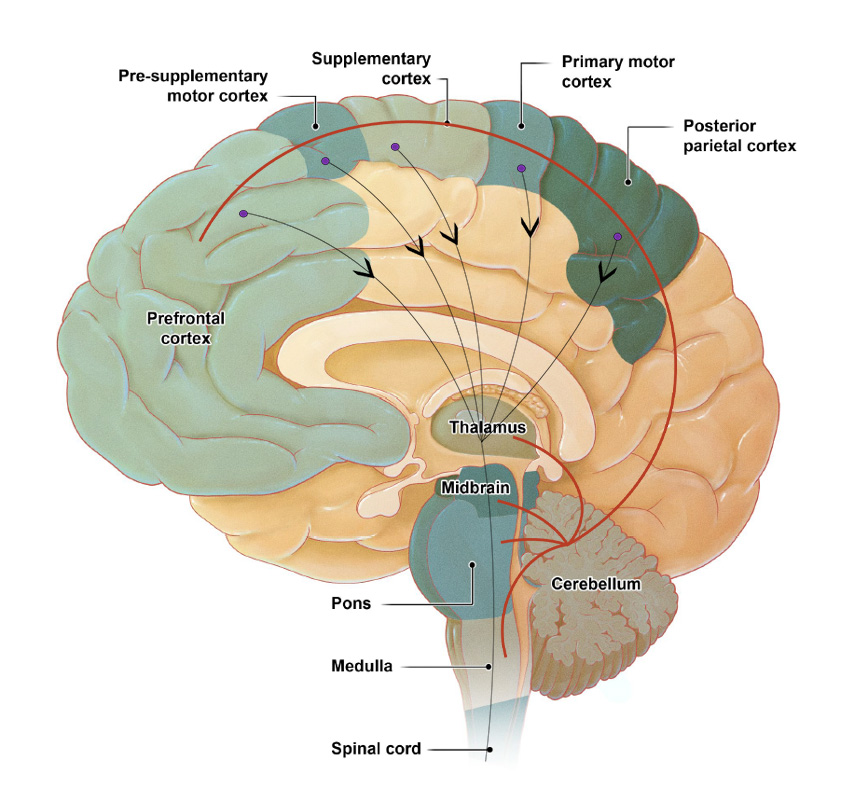
Gait control requires activation of nearly the entire nervous system and musculoskeletal system.
This function is regulated by automatic and voluntary processes.
The cerebellum regulates the cognitive and automatic processes of posture-gait control by acting on the cerebral cortex and the brainstem, respectively.
Voluntary movements result from intentional motor signals traveling from the cerebral cortex to the brainstem and spinal cord.
This voluntary process is always linked to automatic mechanisms of postural control including balance adjustment and muscle tone regulation controlled by the limbic system, the brainstem, and the spinal cord.
Gait Deficit in MS
Walking impairment is a hallmark feature of MS and a common method of monitoring the progress of disease and neurological disability in MS; gait deficits are common in people with MS, irrespective of disease course, and are one of the main causes of disability.
In a study assessing the disruptive effects of individual MS-associated problems on the lives of people with MS who experience these problems at least twice a week, individuals report walking impairment/motor disability as one of the most impactful consequences of their disease.
Patients most frequently rate walking as the bodily function of greatest importance, valued more highly than vision, thinking and memory, and speech, regardless of level of disability or disease duration.
REFERENCES:
Larocca NG. Impact of walking impairment in multiple sclerosis: perspectives of patients and care partners. Patient. 2011;4(3):189‒201. Motl RW, Learmonth YC. Neurological disability and its association with walking impairment in multiple sclerosis: brief review. Neurodegener Dis Manag. 2014;4(6):491‒500.
Cameron MH, Nilsagard Y. Balance, gait, and falls in multiple sclerosis. Handb Clin Neurol. 2018;159:237‒250.
Myhr KM, Riise T, Vedeler C, et al. Disability and prognosis in multiple sclerosis: demographic and clinical variables important for the ability to walk and awarding of disability pension. Mult Scler. 2001;7(1):59‒65.
Takakusaki K. Neurophysiology of gait: from the spinal cord to the frontal lobe. Mov Disord. 2013;(11):1483–1491.
Takakusaki K. Functional neuroanatomy for posture and gait control. J Mov Disord. 2017;10(1):1–17.
Barthélemy D, Grey MJ, Nielsen JB, Bouyer L. Involvement of the corticospinal tract in the control of human gait. Prog Brain Res. 2011;192:181–197.
